Beet root juice as a natural red colorant
Beet root juice is a natural colorant of intense red to purple color. Beet root is the main commercial source of natural red food color, and it is commonly used in food and the pharmaceutical & cosmetic industry. This natural red colorant can be easily prepared at home and it is suitable for use in preparation of food and handmade cosmetics.
Beet root pigments called betalains are water-soluble. They are found in the vacuole juice of beet root cells and readily leak out when the cells get damaged. Betalains are a class of various pigments of yellow, orange, reddish and purple color. Fresh beet juice contains around 1g/lit (0.1%) betalains in total. Red colored betanin (also called ‘beetroot red’) is the most abundant amongst them, giving the beet root juice its characteristic purple-red color.
Beet root juice properties:
Color obtained: shades of pink to purple-red, depending of concentration and color of other ingredients in formulation
Solubility: water soluble; insoluble in oils
Stability: stable in acidic formulations; sensitive to alkalis, heat, oxygen and light
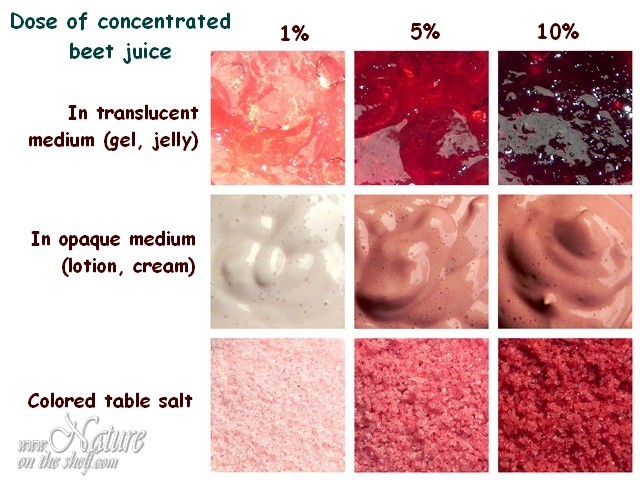
Dosage: 1-10% of the total weight of formulation
Beet pigments are unstable and sensitive to environment influences. They begin to degrade immediately after extraction from beet root cells due to exposure to enzymes, oxygen and light. Their best stability is in acidic environment, at pH 4.2-5.0. They rapidly degrade in alkaline environment (pH above 7), leaving a solution of yellowish-brown color.
Beet juice pigments are also sensitive to thermal processing; if exposed to temperature above 50oC (122oF), they start to break down. When exposed to 100oC/212oF (boiling temperature), more than 80% of red pigment will be lost within three hours. Pigment loss during short-term exposure to high temperature (pasteurization or quick boiling) is not significant enough for visible color change.
Use
Poor stability of beet root pigments determines the possibility of their use in food and cosmetics. Their use is limited to acidic, water-based products which do not need additional thermal processing after the colorant is added, and which can be stored away from heat, air and light. Anyway, with time their color inevitably evolves to yellowish-brown or even gray, which is accelerated if products are exposed to light, air and/or heat, and if the product pH is above 5.
Beet root juice used in cosmetic formulations yields shades of pink to purple-red color. It is easily soluble in water (including hydrosols, floral waters and aloe vera gel) and suitable for coloring of:
- Liquid water-based preparations like shower gels, lotions, creams, bubble baths &
- Dry preparations like bath salts or blushes.
Due to its degradation in alkaline environment, it is not suitable for coloring soap made from scratch (CP, HP), because in contact with lye it will oxidize to tannish-brown color.

How to make homemade beet juice colorant
There are a few variations in making homemade beet juice colorant, and it is entirely up to you to choose which one is the most suitable for you. The basic thing is, of course, to squeeze out the juice of the beet root. Variations are in the way how beet is prepared before squeezing, and in the possibilities for juice concentration and preservation.
You can use raw beet roots, or you can preheat them in microwave. Preheating softens the roots and makes extraction easier. As beet pigments are heat sensitive, however, expect a certain portion of pigments to be destroyed.
1st method: cold pressing
Wash and peel fresh beet roots. Grate them and squeeze out the juice using a kitchen press, or blend the beet roots using a kitchen processor and squeeze out the juice with the help of a cheese cloth. The juice extracted in either of the two ways retains the highest pigment content, but it also requires more effort than extraction from preheated roots.
2nd method: extraction from preheated roots
Wash and peel beet roots. Chop the roots in small pieces and heat them in a microwave 3-4 times, 2-3 min at a time; cool between heating. Let it cool and squeeze out the juice using a cheese cloth or kitchen press. Preheating of beet roots destroys a small portion of red pigments. This is not apparent in freshly prepared juice, but it will affect color longevity.
Optional: preservation
Beet root juice intended for use as a food colorant is best to use freshly prepared and to consume within one day as any other fresh food. If it is intended for use in cosmetics, it is necessary to be preserved.
As any freshly prepared, unprocessed juice, beet root juice is prone to quick spoiling at room temperature if unpreserved. It can be kept in the refrigerator for 1-2 days. Quick boiling (roll boiling for 2-3 min) will kill some (but not all) yeasts, moulds and bacteria, so its shelf-life will be prolonged for 1-2 days, but even so it has to be refrigerated and won’t last longer than a few days.
Beet juice intended for coloring cosmetics must withstand long-term exposure to room temperature. In such case, adjust its acidity to pH 4-4.5 using citric acid, boil it quickly and add some cosmetic-grade preservative intended for use in acidic formulations.
Optional: concentration
To obtain more concentrated beet juice, naturally occurred water in it should be evaporated carefully, in order to minimize pigment degradation by heat. Any thermal treatment of beet juice over 50oC (122oF) leads to decomposition of a portion of beet pigments. Concentration can be achieved either by long-term exposure to 50oC (122oF) temperature or by quick boiling. In both cases, the juice should be poured into a large baking dish in a thin layer to maximize evaporation surface.
Evaporation at low temperature can be achieved by using the oven at 50oC (122oF) for several hours. Previously, the juice should be boiled quickly in order to prevent spoilage and pigment deterioration due to enzymes and yeasts.
Evaporation by boiling should last for no more than 10-15 min because beet pigments quickly degrade at high temperature.
Before evaporation, add citric acid to adjust beet juice acidity to pH 4-4.5. This will reduce pigment degradation caused by adverse pH.
Storage:
For long-term storage, beet juice should be preserved and kept in airtight bottles or jars, in a cold and dark place. If stored properly, it can retain its color for several months.